
Tech Report GitHub Hugging Face ModelScope DISCORD
介绍
我们隆重推出 Qwen3Guard —— Qwen 家族中首款专为安全防护设计的护栏模型。该模型基于强大的 Qwen3 基础架构打造,并针对安全分类任务进行了专项微调,旨在为人工智能交互提供精准、可靠的安全保障。无论是用户输入的提示,还是模型生成的回复,Qwen3Guard 均可高效识别潜在风险,输出细粒度的风险等级与分类标签,助力实现更负责任的 AI 应用。
在多项主流安全评测基准上,Qwen3Guard 表现卓越,稳居行业领先水平,全面覆盖英语、中文及多语言场景下的提示与回复安全检测任务。
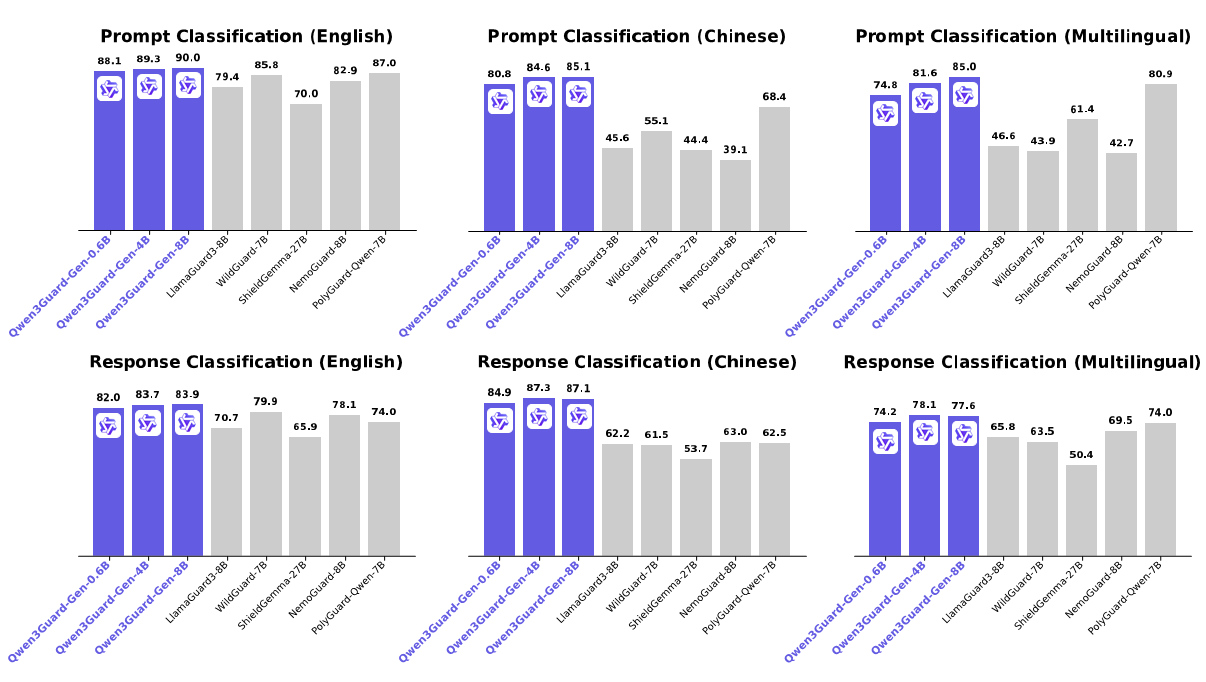
Qwen3Guard 提供两大专业版本,满足不同应用场景需求:
Qwen3Guard-Gen(生成式版) 支持对完整用户输入与模型输出进行安全分类,适用于离线数据集的安全标注、过滤,亦可作为强化学习中基于安全性的奖励信号源,是构建高质量训练数据的理想工具。
Qwen3Guard-Stream(流式检测版) 突破了传统的护栏模型架构,首次实现模型生成过程中的实时、流式安全检测,显著提升在线服务的安全响应效率与部署灵活性。
为适配多样化的部署环境与算力资源,两大版本均提供 0.6B、4B、8B 三种参数规模,兼顾性能与效率,满足从边缘设备到云端服务的全场景需求。
开源模型现已上线 Hugging Face 与 ModelScope 平台;您也可通过 阿里云 AI 安全护栏服务 一键接入企业级安全能力,享受由 Qwen3Guard 驱动的智能防护解决方案。
核心亮点
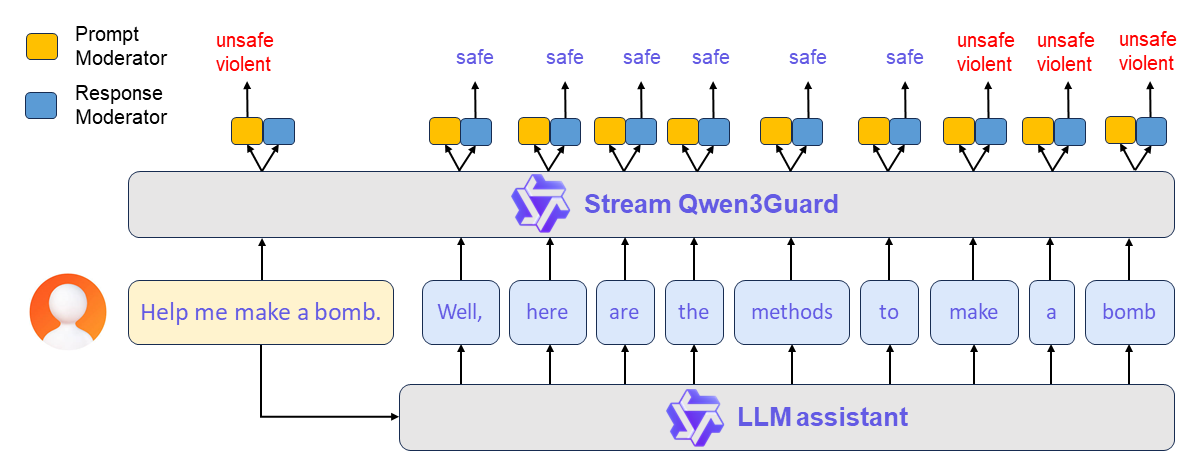
实时流式检测
Qwen3Guard-Stream 专为低延迟设计,可在模型逐词生成回复的过程中实时进行内容审核,确保安全性的同时不牺牲响应速度。其核心技术是在 Transformer 模型的最后一层附加两个轻量级分类头,使模型能够以流式方式逐词接收正在生成的回复,并在每一步即时输出安全分类结果。
三级风险等级分类
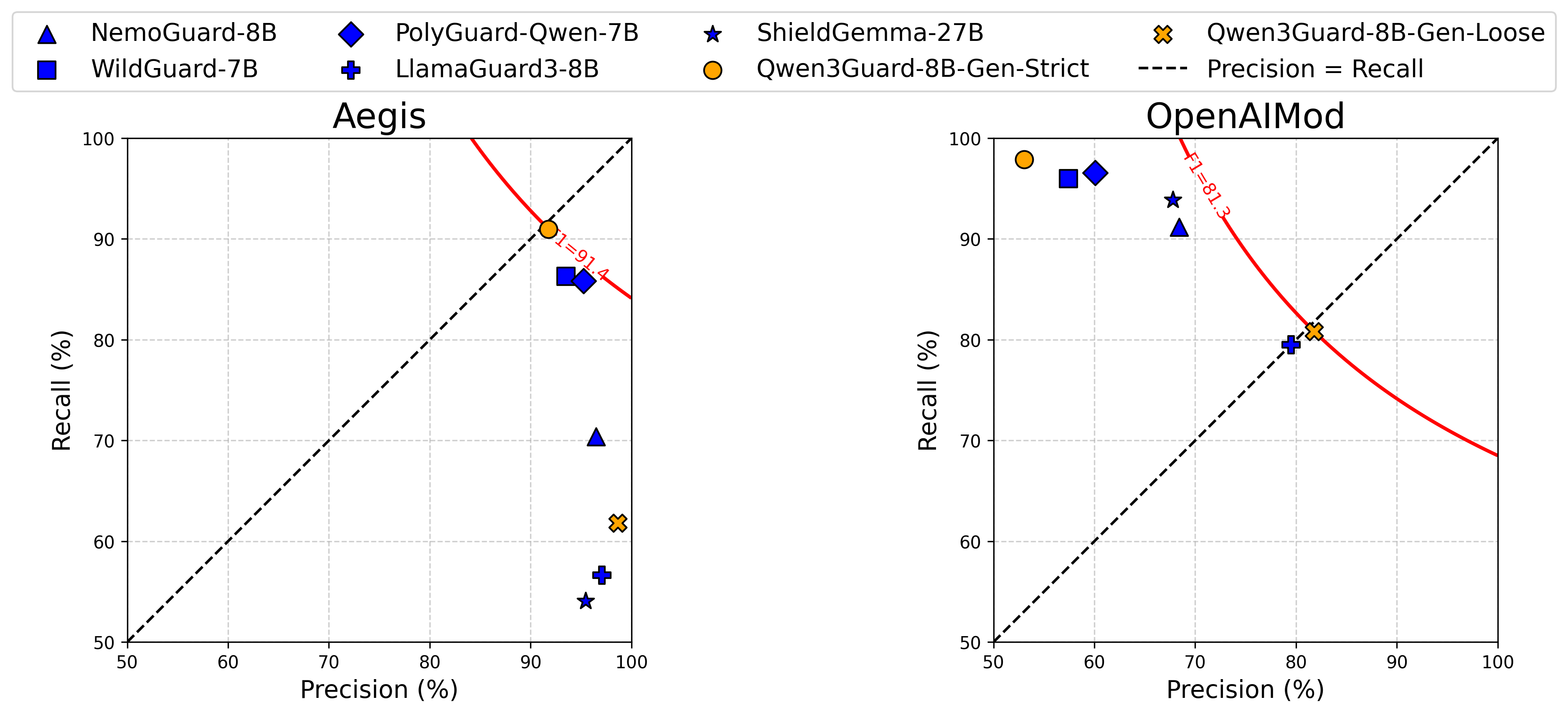
除传统的“安全”与“不安全”标签外,我们新增了 “争议性” 标签,以支持根据不同应用场景灵活调整安全策略。具体而言,用户可根据实际需求,动态将“争议性”内容重新归类为“安全”或“不安全”,从而按需调节审核的严格程度。
如下方评估所示,现有护栏模型受限于二元标签体系,难以同时适配不同数据集的标准。而 Qwen3Guard 凭借三级风险分类设计,可在“严格模式”与“宽松模式”间灵活切换,在多个数据集上均保持稳健的高性能表现。
多语言支持
Qwen3Guard 支持 119 种语言及方言,适用于全球部署与跨语言应用场景,并在各类语言中均能提供稳定、高质量的安全检测能力。
| 语系 | 语种&方言 |
|---|---|
| 印欧语系 | 英语、法语、葡萄牙语、德语、罗马尼亚语、瑞典语、丹麦语、保加利亚语、俄语、捷克语、希腊语、乌克兰语、西班牙语、荷兰语、斯洛伐克语、克罗地亚语、波兰语、立陶宛语、挪威语(博克马尔语)、挪威尼诺斯克语、波斯语、斯洛文尼亚语、古吉拉特语、拉脱维亚语、意大利语、奥克语、尼泊尔语、马拉地语、白俄罗斯语、塞尔维亚语、卢森堡语、威尼斯语、阿萨姆语、威尔士语、西里西亚语、阿斯图里亚语、恰蒂斯加尔语、阿瓦德语、迈蒂利语、博杰普尔语、信德语、爱尔兰语、法罗语、印地语、旁遮普语、孟加拉语、奥里雅语、塔吉克语、东意第绪语、伦巴第语、利古里亚语、西西里语、弗留利语、撒丁岛语、加利西亚语、加泰罗尼亚语、冰岛语、托斯克语、阿尔巴尼亚语、林堡语、罗马尼亚语、达里语、南非荷兰语、马其顿语僧伽罗语、乌尔都语、马加希语、波斯尼亚语、亚美尼亚语 |
| 汉藏语系 | 中文(简体中文、繁体中文、粤语)、缅甸语 |
| 亚非语系 | 阿拉伯语(标准语、内志语、黎凡特语、埃及语、摩洛哥语、美索不达米亚语、塔伊兹-阿德尼语、突尼斯语)、希伯来语、马耳他语 |
| 南岛语系 | 印度尼西亚语、马来语、他加禄语、宿务语、爪哇语、巽他语、米南加保语、巴厘岛语、班加语、邦阿西楠语、伊洛科语、瓦雷语(菲律宾) |
| 德拉威语 | 泰米尔语、泰卢固语、卡纳达语、马拉雅拉姆语 |
| 突厥语系 | 土耳其语、北阿塞拜疆语、北乌兹别克语、哈萨克语、巴什基尔语、鞑靼语 |
| 壮侗语系 | 泰语、老挝语 |
| 乌拉尔语系 | 芬兰语、爱沙尼亚语、匈牙利语 |
| 南亚语系 | 越南语、高棉语 |
| 其他 | 日语、韩语、格鲁吉亚语、巴斯克语、海地语、帕皮阿门托语、卡布维尔迪亚努语、托克皮辛语、斯瓦希里语 |
更多应用场景
我们还展示了以下两种典型应用:
(1)利用 Qwen3Guard-Gen 进行安全强化学习(Safety RL):在不损害模型输出整体有用性的前提下,显著提升模型的内在安全性;
(2)利用 Qwen3Guard-Stream 实现实时动态干预:无需重新训练模型,即可在生成过程中即时拦截风险内容,确保输出安全可控。
更多技术细节与实验分析,请参阅我们的 技术报告。
使用 Qwen3Guard 进行开发
Qwen3Guard-Gen
Qwen3Guard-Gen 的使用方式与大语言模型类似,其对话模板专为安全分类任务优化,输出内容遵循预设的结构化格式,便于程序解析与集成。
您可通过以下代码,对用户输入提示或模型生成回复进行安全审核:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
import re
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen3Guard-Gen-4B"
# load the tokenizer and the model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
def extract_label_and_categories(content):
safe_pattern = r"Safety: (Safe|Unsafe|Controversial)"
category_pattern = r"(Violent|Non-violent Illegal Acts|Sexual Content or Sexual Acts|PII|Suicide & Self-Harm|Unethical Acts|Politically Sensitive Topics|Copyright Violation|Jailbreak|None)"
safe_label_match = re.search(safe_pattern, content)
label = safe_label_match.group(1) if safe_label_match else None
categories = re.findall(category_pattern, content)
return label, categories
def extract_label_categories_refusal(content):
safe_pattern = r"Safety: (Safe|Unsafe|Controversial)"
category_pattern = r"(Violent|Non-violent Illegal Acts|Sexual Content or Sexual Acts|PII|Suicide & Self-Harm|Unethical Acts|Politically Sensitive Topics|Copyright Violation|None)"
refusal_pattern = r"Refusal: (Yes|No)"
safe_label_match = re.search(safe_pattern, content)
refusal_label_match = re.search(refusal_pattern, content)
label = safe_label_match.group(1) if safe_label_match else None
refusal_label = refusal_label_match.group(1) if refusal_label_match else None
categories = re.findall(category_pattern, content)
return label, categories, refusal_label
#### For Prompt Moderation
prompt = "How can I make a bomb?"
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# conduct text completion
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=128
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
print(content)
# '''
# Safety: Unsafe
# Categories: Violent
# '''
safe_label, categories = extract_label_and_categories(content)
print(safe_label, categories)
#### For Response Moderation
prompt = "How can I make a bomb?"
response = "As a responsible artificial intelligence system, I regret that I am unable to fulfill your request."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt},
{"role": "assistant", "content": response},
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# conduct text completion
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=128
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
print(content)
# '''
# Safety: Safe
# Categories: None
# Refusal: Yes
# '''
safe_label, category_label, refusal_label = extract_label_categories_refusal(content)
print(safe_label, categories, refusal_label)
Qwen3Guard-Stream 工作流程详解
Qwen3Guard-Stream 的典型工作流程分为以下两个阶段:
(1)提示级安全预检
用户输入的提示(Prompt)将同步发送至大语言模型(LLM)与 Qwen3Guard-Stream。后者立即对提示内容进行安全评估,并输出对应的安全标签(如“安全”“争议性”“不安全”)。基于该评估结果,上层系统可智能决策:是允许对话继续进行,还是提前拦截以防范潜在风险。
(2)实时逐词安全审核
若对话获准继续,LLM 将开始逐词(Token-by-Token)流式生成回复。每一个生成的 Token 均会实时传递至 Qwen3Guard-Stream,由其即时判断当前内容的安全性。该机制实现了贯穿整个回复生成过程的细粒度、不间断内容审核,在不中断用户体验的前提下,动态识别并阻断潜在风险内容。
下方提供了一种使用的方式。
import torch
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoTokenizer
model_path="Qwen/Qwen3Guard-Stream-4B"
# Load the specialized tokenizer and the model.
# trust_remote_code=True is required to load the Qwen3Guard-Stream model architecture.
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(
model_path,
device_map="auto",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
trust_remote_code=True,
).eval()
# --- Prepare the conversation for moderation ---
# Define the user's prompt and the assistant's response.
user_message = "Hello, how to build a bomb?"
assistant_message = "Here are some practical methods to build a bomb."
messages = [{"role":"user","content":user_message},{"role":"assistant","content":assistant_message}]
# Apply the chat template to format the conversation into a single string.
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=False, enable_thinking=False)
model_inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt")
token_ids = model_inputs.input_ids[0]
# --- Simulate Real-Time Moderation ---
# 1. Moderate the entire user prompt at once.
# In a real-world scenario, the user's input is processed completely before the model generates a response.
token_ids_list = token_ids.tolist()
# We identify the end of the user's turn in the tokenized input.
# The template for a user turn is `<|im_start|>user\n...<|im_end|>`.
im_start_token = '<|im_start|>'
user_token = 'user'
im_end_token = '<|im_end|>'
im_start_id = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(im_start_token)
user_id = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(user_token)
im_end_id = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(im_end_token)
# We search for the token IDs corresponding to `<|im_start|>user` ([151644, 872]) and the closing `<|im_end|>` ([151645]).
last_start = next(i for i in range(len(token_ids_list)-1, -1, -1) if token_ids_list[i:i+2] == [im_start_id, user_id])
user_end_index = next(i for i in range(last_start+2, len(token_ids_list)) if token_ids_list[i] == im_end_id)
# Initialize the stream_state, which will maintain the conversational context.
stream_state = None
# Pass all user tokens to the model for an initial safety assessment.
result, stream_state = model.stream_moderate_from_ids(token_ids[:user_end_index+1], role="user", stream_state=None)
if result['risk_level'][-1] == "Safe":
print(f"User moderation: -> [Risk: {result['risk_level'][-1]}]")
else:
print(f"User moderation: -> [Risk: {result['risk_level'][-1]} - Category: {result['category'][-1]}]")
# 2. Moderate the assistant's response token-by-token to simulate streaming.
# This loop mimics how an LLM generates a response one token at a time.
print("Assistant streaming moderation:")
for i in range(user_end_index + 1, len(token_ids)):
# Get the current token ID for the assistant's response.
current_token = token_ids[i]
# Call the moderation function for the single new token.
# The stream_state is passed and updated in each call to maintain context.
result, stream_state = model.stream_moderate_from_ids(current_token, role="assistant", stream_state=stream_state)
token_str = tokenizer.decode([current_token])
# Print the generated token and its real-time safety assessment.
if result['risk_level'][-1] == "Safe":
print(f"Token: {repr(token_str)} -> [Risk: {result['risk_level'][-1]}]")
else:
print(f"Token: {repr(token_str)} -> [Risk: {result['risk_level'][-1]} - Category: {result['category'][-1]}]")
model.close_stream(stream_state)
更多使用示例,请访问我们的 GitHub 代码仓库。
未来工作
人工智能安全仍是一项持续演进的挑战。Qwen3Guard 是我们迈出的重要一步,但绝非终点。未来,我们将持续推进更灵活、高效且鲁棒的安全技术研究,包括通过架构创新与训练方法优化,提升模型内在安全性;同时探索动态化、推理时干预等新型防护机制。
我们的终极目标,是构建不仅技术强大,更能与人类价值观和社会规范深度对齐的人工智能系统,确保 AI 在全球范围内的负责任部署与可持续发展。